Atopic Dermatitis: Home Remedies, OTC Options, and Lifestyle Tips for Healthier Skin
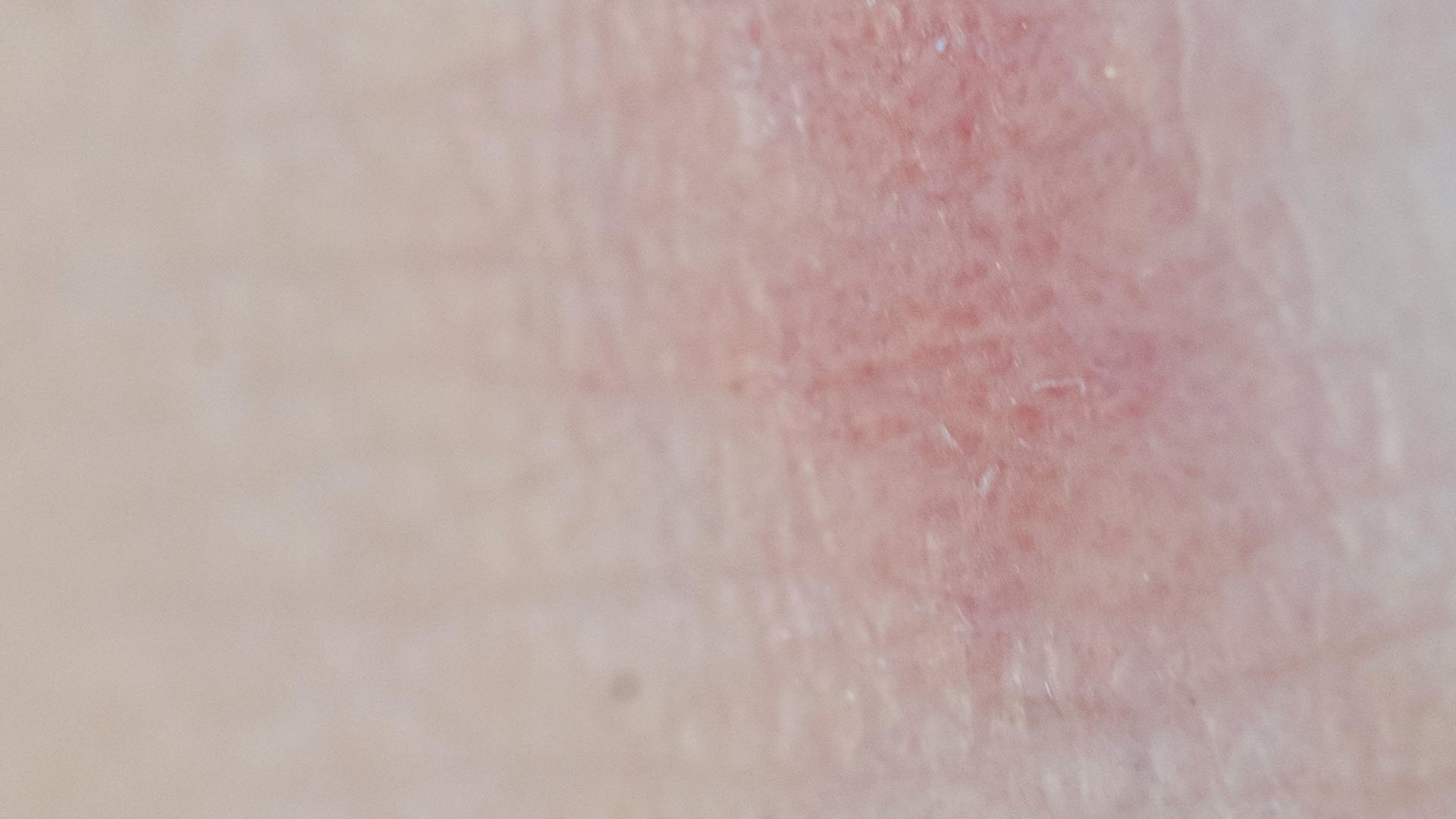
Atopic dermatitis, more commonly known as eczema, is a widespread skin condition that causes inflamed, itchy, and irritated skin.
Though its official name may not always be recognized, its symptoms are unmistakable. Persistent itching, redness, swelling, and sometimes cracked skin can make this condition extremely uncomfortable, and can even affect daily quality of life.
Atopic dermatitis can develop on nearly any part of the body, including the face, hands, elbows, knees, and neck. The severity can vary greatly — some people experience only mild irritation, while others suffer from intense flare-ups that require medical intervention.
Common Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but several factors are known to contribute:
- Genetics: A family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever increases the risk.
- Immune system dysfunction: An overactive immune response leads to inflammation and skin barrier breakdown.
- Environmental triggers: Such as pollen, mold, dust mites, and pet dander.
- Skin barrier defects: Skin loses moisture more easily, making it vulnerable to irritants and allergens.
- Harsh soaps, detergents, or skincare products that strip away natural oils.
- Weather changes, particularly dry or cold climates, which dry out the skin.
- Stress: Emotional stress can trigger or worsen flare-ups.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While many cases of atopic dermatitis can be managed at home, you should consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Severe or widespread rashes that interfere with daily activities.
- Signs of infection such as pus, yellow crusting, or fever.
- Persistent itching that causes significant sleep disruption.
- Thickened, leathery skin that doesn't improve with moisturizers or OTC treatments.
- Rashes around the eyes, lips, or genital area.
Prompt medical treatment can prevent complications like secondary bacterial infections or permanent skin damage.
First Aid for Eczema Flare-Ups
If you experience a sudden flare-up of atopic dermatitis:
- Gently cleanse the area with lukewarm water and a fragrance-free cleanser.
- Apply a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer immediately after washing while the skin is still damp.
- Avoid scratching — it can lead to infection and worsen inflammation. Use a cold compress to ease itching instead.
- Wear loose, soft clothing made of cotton to avoid irritating sensitive skin.
- Use OTC hydrocortisone cream for mild flares if needed (no longer than 7 days without consulting a doctor).
Lifestyle Tips for Managing Atopic Dermatitis
Moisturize Frequently
Moisturizing is critical for managing eczema. Apply a thick, hydrating cream or ointment at least twice a day, and always after bathing to lock in moisture.
Avoid Triggers
Identify and minimize exposure to irritants like harsh soaps, synthetic fabrics, pet dander, dust mites, and stress where possible.
Choose Gentle Products
Use fragrance-free and hypoallergenic soaps, shampoos, and detergents to minimize skin irritation.
Shower Smart
Take lukewarm showers rather than hot baths, and limit shower time to 10–15 minutes. Always gently pat (do not rub) the skin dry with a soft towel.
Wear Breathable Clothing
Natural fabrics like cotton are less irritating than synthetic fibers. Loose clothing also prevents friction against sensitive skin.
Manage Stress
Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, yoga, or meditation to lower stress levels and prevent flare-ups linked to emotional triggers.
Protect Skin in Dry Weather
Use a humidifier during winter months or in dry climates to maintain moisture in the air and prevent skin from drying out.
When to Avoid Certain Remedies
- Avoid applying raw essential oils directly to eczema patches without diluting them — they can worsen irritation.
- Skip hot showers or baths that strip away natural oils and further dry out the skin.
- Don’t overuse topical steroids — prolonged use can thin the skin. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully.
- Avoid heavily fragranced products and "natural" soaps with irritants like citrus or mint unless tested first.
Dietary Support for Healthier Skin
- Omega-3 fatty acids (from fatty fish, flaxseeds, or supplements) can reduce systemic inflammation.
- Probiotic-rich foods (like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables) may help balance the immune system.
- Vitamin D supplementation is associated with improved skin health in some people with eczema, especially in colder months.
- Antioxidant-rich foods (berries, leafy greens, nuts) help fight inflammation and support skin healing.
Home Remedies for Atopic Dermatitis
Living with atopic dermatitis can be challenging. Still, by combining natural home remedies, targeted OTC treatments, and healthy lifestyle adjustments, you can help reduce flare-ups and improve the health of your skin. Focus on gentle care, stay hydrated inside and out, avoid known triggers, and don’t hesitate to seek medical support when needed. Taking a proactive, informed approach will help you manage eczema with greater confidence and comfort.
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is a powerful natural moisturizer that contains lauric acid, an antibacterial agent. Applying virgin coconut oil daily helps lock in moisture and protect against infection, reducing redness and itchiness associated with atopic dermatitis.
Oatmeal Baths
Colloidal oatmeal soothes inflamed, irritated skin. Add finely ground oatmeal to lukewarm bathwater and soak for 10–15 minutes. Oatmeal creates a protective barrier on the skin, helping to reduce itching and dryness.
Spearmint Leaves
Spearmint leaf juice can calm irritated skin. Crush fresh spearmint leaves, mix with a small amount of water, and apply gently to the affected areas. The cooling sensation and anti-inflammatory properties can ease itching during flare-ups.
Papaya Seeds
Mashed papaya seeds create a natural anti-inflammatory paste that can be applied to eczema patches. This simple remedy may help reduce swelling and curb the intense urge to scratch.
Aloe Vera Gel
Pure aloe vera gel offers cooling, healing properties. Aloe reduces inflammation and helps repair damaged skin when applied directly to areas affected by eczema.
Honey
Raw honey is a natural antimicrobial and healing agent. Apply a thin layer of honey to affected areas of eczema to soothe irritated skin and promote faster healing.
Sunflower Seed Oil
Sunflower oil boosts the skin’s natural barrier and retains moisture. Gently apply to damp skin after bathing to keep skin supple and reduce irritation.
Over-the-Counter Options for Atopic Dermatitis
- Hydrocortisone creams: Reduce redness, itching, and inflammation during mild flare-ups.
- Antihistamines (like loratadine or diphenhydramine): Help control severe itching and aid sleep during intense flare-ups.
- Moisturizing creams and ointments: Look for products labeled "fragrance-free" and "for sensitive skin." Brands like Cetaphil, CeraVe, and Eucerin are dermatologist-recommended.
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors (like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus): Available by prescription but increasingly discussed as part of a stepwise approach.